Quantum
Resolve problems that cannot be efficiently calculated with existing supercomputers to quickly solve problems in areas where answers were difficult to find
Quantum Computer
Quantum technology, following artificial intelligence,
will be the game changer of future industries
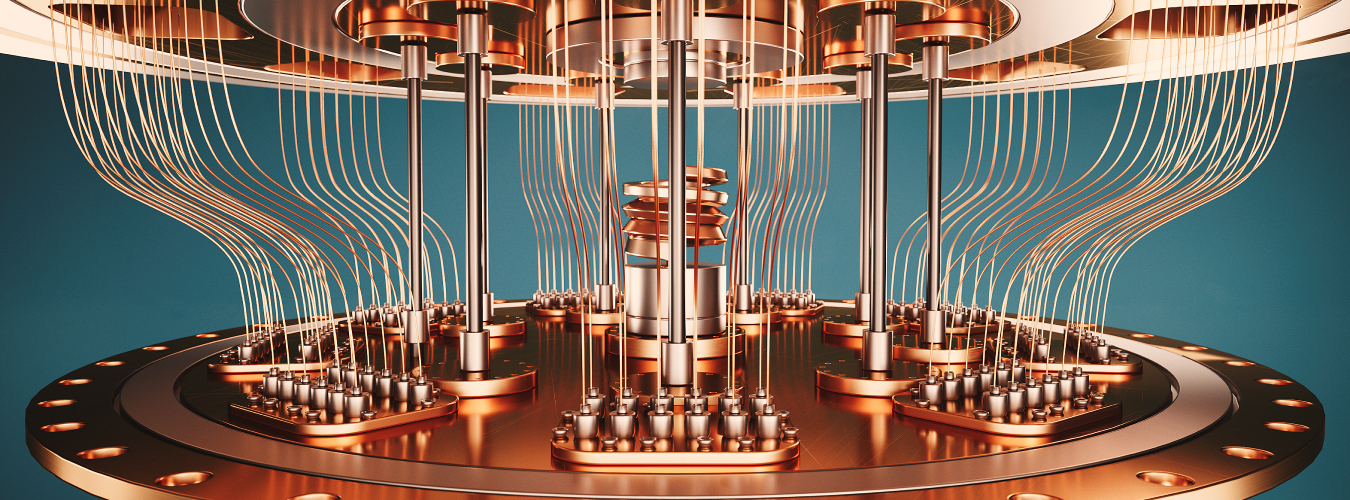
A quantum computer is a computer processing device proposed to use the characteristics of quantum mechanics to solve computational problems in areas that are impossible or difficult to process with classical computers.
The quantum mechanical principles that form the basis of quantum computers are quantum superposition, observational collapse, and quantum entanglement.
-
Quantum Superposition
-
In classical information devices, information is expressed as 0 or 1, and the quantum state can express information in the form of a simultaneous linear combination of 0 and 1. This feature is also expressed as 'quantum parallelism'.
-
Observation Collapse
-
Observation causes irreversible changes in the quantum state, preventing the original quantum state from being restored after measurement and making replication impossible. This ensures information security by perfectly preventing external measurement, making it widely applicable in the field of quantum cryptography.
-
Quantum Entanglement
-
In the phenomenon where if one state is determined in two or more quantum states, the other dependent states are determined accordingly, interference occurs between spatially separated information in the process of information processing and communication.
Principles of Quantum Computers
-
Classical Computer
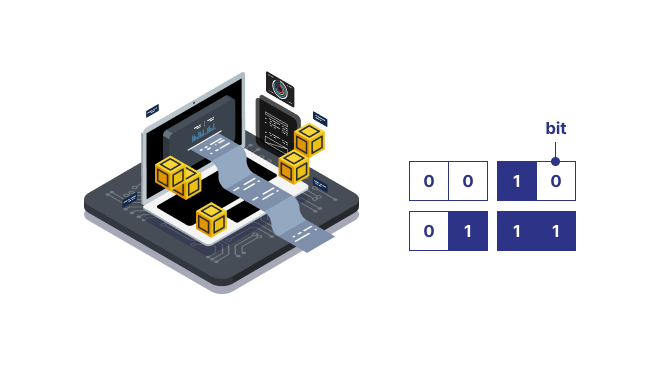
Recognizes either 0 or 1 as a unit of information called a bit for computation. With 2 bits, it processes only one piece of information among 00, 01, 10, or 11.
-
Quantum Computer
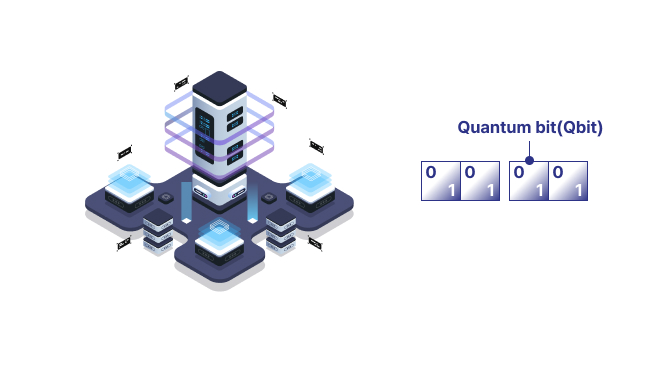
Performs operations using bits (qubits) of quantum states where 0 and 1 exist simultaneously. With 2 qubits, the 4 pieces of information 00, 01, 10, 11 exist simultaneously. Problems that take hundreds of millions of years to solve with supercomputers can be calculated in just a few hours.
Changes in Quantum Technology

-
 2035
2035
Quantum Computer
 2030
2030
Quantum Cryptography Communication
 2025
2025
Quantum Sensors
-
Conventional Technology
-
-
1,024-bit encryption decryption in 1 million years
Power consumption 30MW -
International wiretapping occurs through undersea fiber optic cables,
Hacking of wireless communications like NFC, satellite communication is possible -
Identification of cancer cells smaller than 5mm with MRI
Detection within about 100m with LiDAR, cannot penetrate
-
-
Quantum Era Technological Changes
-
- Ultra-fast computation
1,024-bit encryption decryption in 10 hours
Power consumption 0.05MW (1/600) - Ultra-reliable security
With a quantum encryption key method that gets destroyed upon wiretapping,
Completely prevents illegal wiretapping and hacking - Ultra-precise measurement
Identification of cancer cells smaller than 0.05mm with Quantum MRI
Detection over 45km with Quantum Imaging Sensors
- Ultra-fast computation
Applications of Quantum Technology

-
Finance
- Investment Portfolio Optimization
- Risk Management
- Options and pricing

-
Chemistry
- Molecular design optimization
- Quantum Mechanics of Chemical Reactions
- Simulation
- Optimization of cells and catalysts

-
Medical treatment
- Drug discovery/optimal dosage calculation for cancer treatment
- Speeding up personalized medicine

-
IT
- Fast clustering for machine learning
- Fast learning of image recognition

-
distribution
- Optimization of logistics for airplanes, ships, trucks, etc.
- Real-time traffic analysis and guidance

-
Pharmaceuticals
- 3D structure of proteins
- Optimization/analysis simulation (development of special drugs for Alzheimer's disease, etc.)
- New drug/catalyst development
- Cancer prevention through genetic analysis

-
Automobile
- Electric Car Battery Design
- Automobile Design Engineering
- Optimization of Urban Transportation Services

-
Aerospace
- Hydrodynamically optimized airframe design
- Aviation Rowing Simulation
- Bug-catching optimization of the flight control system

-
Energy
- Optimization of power transmission grid and energy distribution
